Biomag - Encyclopedia - Slipped disc
Slipped disc - symptoms, description and treatment

Author MUDr. Peter Bednarčík CSc.
Revision

Do you feel that back pain has become an integral part of your life? Is it an uncomfortable back pain that shoots up your legs or arms? Is it accompanied by tingling in the limbs and muscle weakness? These problems may indicate a slipped disc (prolapsed intervertebral disc.) [1]
Let’s look at how to recognize the symptoms of a herniated disc, find out its causes and treatment options. How to suppress symptoms such as pain, swelling and inflammation that are related to this disease? This knowledge can help you regain control of your health and comfort. Read more here.
Slipped disc symptoms
- Severe pain at the site of the bulging
- Pain shoots to the extremities
- Tingling in the limbs
- Prickling sensation
- Changes in sensitivity of the limbs
- Muscle weakness
- Difficulty walking
It can occur in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine. [2] A disc protrusion is usually very painful, but the specific discomfort varies depending on the size of the protrusion and where it occurred. [3]

Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis. Do not use this or any other article on the internet to make a diagnosis. Do not delay seeing a doctor and address your condition early.
Description and causes of a herniated disc
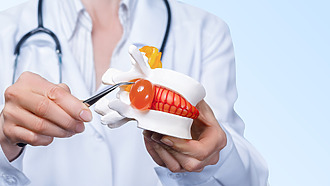
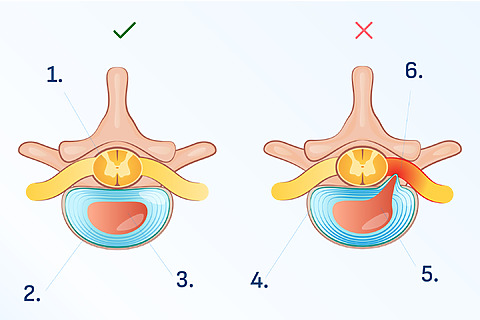
Slipped disc – what is it?
The intervertebral disc is a flexible tissue that connects the vertebrae and allows the spine to move smoothly. The disc has a jelly-like nucleus that is encased in a tough ring.[4] If the soft nucleus gets out of its “shell,” it irritates the surrounding nerves and causes pain. [5]
A bulging disc can cause pain in different parts of the body. It depends on where the protrusion occurred.
- A disc protrusion in the cervical spine causes severe pain in the neck.
In addition, the pain often shoots into the shoulders, arms and fingers. The pain may worsen with certain neck movements. [6] - A slipped disc in the lower back brings severe pain in the hips.
Other symptoms of it in the lumbar spine are: pain in the buttocks, hips or thighs, muscle weakness and difficulty walking.[7] - In addition to pain directly at the thoracic spine, a slipped disc in the thoracic spine causes discomfort in the legs.
Patients feel tingling, tingling and a change in sensation in one or both lower limbs. [8]
Herniated disc - photogallery
Why does disc herniation occur?
Disc protrusion is usually related to wear and tear of the spine. The following risk factors are mainly involved:
- Older age.
With age, the discs lose their elasticity and resistance, which increases the risk of herniation. - Overweight and obesity.
Excessive body weight increases the load on the spine and intervertebral discs, which can lead to wear and tear. - Long-term strain on the spine during work or sports.
Physically demanding work that involves lifting heavy loads, repeated bending and turning, or long periods of sitting can increase pressure on the intervertebral discs. - Lack of exercise and sedentary lifestyle.
Weak and unused back and abdominal muscles cannot effectively support the spine, which can lead to greater stress on the intervertebral discs. - Genetics.
Some people have a genetic predisposition to weakening of the disc tissue, which increases the risk of herniation. [9]
How to diagnose a herniated disc
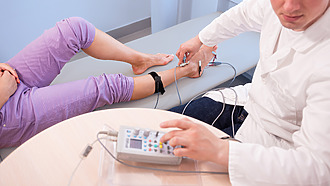
The diagnosis is made by a physician based on a physical examination combined with various imaging methods. The neurologist assesses the type and intensity of pain, checks reflexes, muscle strength and quality of gait.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is a common way to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other causes of the problem.
- The physician may also recommend a CT scan (computed tomography) and an X-ray of the back.
- EMG (electromyography) is used for diagnosis – examination of the electrical activity of muscles and nerves. [10]
Did you know?
- Intervertebral disc herniation most often affects people aged 30 to 50 years. [11]
- The most common problem is a bulging lumbar disc between the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae (L4-L5).
- Also common is a slipeed disc at L5-S1, between the 5th lumbar and 1st sacral vertebrae.[12]
Complications when left untreated
If it is not treated or the treatment is not effective, complications can occur with a significant impact on your life.
- Significant nerve damage may occur.
- It can lead to worsening pain and loss of sensation in the limbs.
- In the most severe cases, it may even adversely affect bladder and bowel function.
- That’s why prevention and spinal care is important. [13]
Nerve damage
Pain in the limbs
Loss of sensitivity in the limbs
Bladder issues

We recommend not postponing treatment of a herniated disc
Do not delay treatment and see a specialist if you have any health problems or doubts about your condition. This will prevent unnecessary health complications.
Herniated disc treatment

How to treat a herniated disc?
In the treatment of herniated intervertebral discs, mainly conservative (non-surgical) methods are used. However, if they do not relieve the patient of pain and the difficulties worsen, surgery may be the solution.[14]
However, in most patients (85%) the acute symptoms of a slipped disc in the cervical spine, thoracic spine or lumbar region disappear within 8 to 12 weeks. [15]
Conservative treatment includes:
- Administration of painkillers and drugs to reduce muscle tension,
- special rehabilitation focused on the affected area,
- regimen measures (adequate physical exertion, application of cold and warm compresses). [16]

Beware
Treatment can only be determined by your physician after considering your overall health. Therefore, do not use this article as a guide to treatment, which can only be determined by your physician.
Rehabilitation of a herniated disc
It focuses on strengthening muscles and restoring spinal mobility. The aim is to minimise the risk of recurrent disc damage and reduce pain. It can last from a few weeks to several months.
May include: physical therapy, cryotherapy, hydrotherapy and other treatment methods.
Rehabilitation after surgery is an important process to regain mobility and return to the activities of normal life.
Herniated disc exercises

Exercise can help relieve pain, reduce inflammation, increase mobility and strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, which can help minimize the risk of further complications and improve quality of life.
It is also important to follow the doctor’s instructions and recommendations regarding exercise and overall treatment, as poorly performed exercise can worsen the condition and lead to complications. [17]
Slipped Disc Exercises:
- Stretching the muscles and spine: Helps relax muscles that may be twisting and putting pressure on nerve fibres.
- Abdominal and back muscle strengthening: helps maintain spinal stability and reduces pressure on the intervertebral discs.
- Aerobic exercise: helps maintain good blood circulation and improves overall body fitness.
- Swimming: Swimming is gentle on the joints and can help strengthen your back muscles.
- Physical therapy: a physical therapy specialist can suggest exercises and procedures that specifically target your needs and condition.
Herniated disc McKenzie exercises
It is an exercise method that was developed specifically for the treatment of back pain, including pain caused by a slipped disc. The exercises are aimed at strengthening and stretching the muscles of the spine and help improve spinal mobility.[18]
The most common McKenzie exercises include:
- Stretching the spine in the prone position:
Lie on your stomach with your arms next to your body. Place your palms on the floor below your shoulders and slowly raise your upper body so that you are resting on your hands. Hold this position for 5-10 seconds, then slowly return to the starting position. - Stretching the spine in the prone position with support:
Lie on your stomach with your arms resting next to your body. Slowly lift your upper body and lean on your elbows. Hold this position for 5-10 seconds, then slowly return to the starting position. - Stretching the spine in the prone position with one side supported:
Lie on your stomach and place one arm under your shoulder on the other side of your body. Slowly lift your upper body and rotate towards the arm that is under your shoulder. Hold this position for 5-10 seconds, then slowly return to the starting position.
McKenzie exercises should be performed under the supervision of a professional such as a physiotherapist or rehabilitation doctor. They must be performed correctly and in accordance with your medical condition. In some cases, McKenzie exercises may be contraindicated, for example, in cases of severe neurological disorders or other health problems.
Herniated disc and sick leave
It can lead to disability. If symptoms are mild, your doctor may recommend staying home for a short time. In cases where the symptoms are severe and the patient is unable to perform their job, the disability may be longer. If the patient is operated on, the patient is usually given sick leave to allow them to recover from the operation.
Prevention of herniated disc
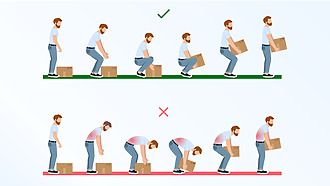
- Maintaining correct posture when standing and sitting,
- lifting heavy objects from a squatting position, not just from a bending position,
- regular physical exercise,
- reasonable body weight. [19]

Important information when dealing with a herniated disc
Spinal wear and tear is a common cause of disc herniation. How to prevent it?
Make sure your posture is correct, especially when sitting for long periods or doing heavy manual work. This will reduce the risk of irreversible changes to your spine. Properly chosen exercises bring relief from the pain of a prolapsed disc and protect the back from further damage to the spine.
Summary and recommendations when dealing with a herniated disc
See your physician
The treatment is always determined by your doctor based on a general examination, an assessment of your condition and an accurate diagnosis.
Causal treatment of herniated disc
After a general examination, your doctor will recommend treatment for the cause of the slipped disc. In connection with this, they will also recommend possible lifestyle modification and further course of action.
Relieving pain, inflammation and promoting healing
Symptomatic treatment focuses on the manifestations or signs (symptoms) of the disease. Such treatment can significantly improve your quality of life and support comprehensive treatment as the disease progresses.
Sources, references and literature
[1] Herniated disc. MayoClinic, 8. February 2022. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/herniated-disk/symptoms-causes/syc-20354095?p=1
[2] Herniated disc. MayoClinic, 8. February 2022. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/herniated-disk/symptoms-causes/syc-20354095?p=1
[3] Herniated disc. American Association of Neurological Surgeons. Available at: https://www.aans.org/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Herniated-Disc
[4] Herniated disc. American Association of Neurological Surgeons. Available at: https://www.aans.org/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Herniated-Disc
[5] Herniated disc. MayoClinic, 8. February 2022. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/herniated-disk/symptoms-causes/syc-20354095?p=1
[6] Herniated disc. American Association of Neurological Surgeons. Available at: https://www.aans.org/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Herniated-Disc
[7] Herniated disc. American Association of Neurological Surgeons. Available at: https://www.aans.org/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Herniated-Disc
[8] Herniated Thoracic Disc. University of Maryland Medical Center. Available at: https://www.umms.org/ummc/health-services/orthopedics/services/spine/patient-guides/herniated-thoracic-disc
[9] Herniated disc. MayoClinic, 8. February 2022. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/herniated-disk/symptoms-causes/syc-20354095?p=1
[10] Herniated disc. MayoClinic, 8. February 2022. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/herniated-disk/symptoms-causes/syc-20354095?p=1
[11] Dydyk A. M., Ngnitewe Massa R., Mesfin F. B. Disc Herniation. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; January 2023. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441822/
[12] Dydyk A. M., Ngnitewe Massa R., Mesfin F. B. Disc Herniation. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; January 2023. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441822/
[13] Herniated disc. MayoClinic, 8. February 2022. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/herniated-disk/symptoms-causes/syc-20354095?p=1
[14] Herniated disc. American Association of Neurological Surgeons. Available at: https://www.aans.org/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Herniated-Disc
[15] Dydyk A. M., Ngnitewe Massa R., Mesfin F. B. Disc Herniation. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; January 2023. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441822/
[16] Herniated disc. MayoClinic, 8. February 2022. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/herniated-disk/symptoms-causes/syc-20354095?p=1
[17] Safe exercises for a herniated disc. Medical NewsToday , 27. January 2019. Available at https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/324311#summary
[18] The McKenzie Method,SpineOne, 7. November 2017. Available at https://spineone.com/mckenzie-method-back-pain
[19] Herniated disc. MayoClinic, 8. February 2022. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/herniated-disk/symptoms-causes/syc-20354095?p=1
| Rate this article |
|
|
5/51 Reviewed by
|
How to reduce pain, inflammation and promote healing?
The solution may be symptomatic treatment using pulsed magnetic therapy (PEMF therapy), which targets symptoms and signs such as pain, swelling and inflammation. In addition, such treatment can support comprehensive treatment and significantly improve quality of life.
Explaining the effects
The basic principle of Biomag 3D pulsed magnetic therapy (PEMF therapy) is the generation of electromagnetic pulses. These pulses penetrate through clothing and through the entire depth of the tissue to the point of targeted application. The pulses have specially developed biotropic parameters (e.g. frequency, shape, intensity) to best affect various health problems.
What are the effects of 3D magnetic therapy (PEMF therapy)?
- Helps relieve pain.
- Mitigates inflammation.
- Suppresses swelling.
How is the treatment applied?
The application is very simple. You select the desired therapeutic effect on the device and attach the attached applicator to the desired application site. Magnetic therapy is usually applied 2 times a day for 20 minutes.
We will be happy to help you try this method and advise you on which device to purchase.