Biomag - Encyclopedia - Nerve compression – chronic
Nerve compression - symptoms, description and treatment

Author MUDr. Peter Bednarčík CSc.
Revision
Do you often wake up with unpleasant sensations such as tingling? Do you often feel a sharp pain when you move that may ease but eventually attacks again? One cause may be nerve compression. Sometimes we talk about a pinched nerve when it is an acute condition that causes significant symptoms, especially pain. The result is limitations in normal daily activities or disturbed sleep.
Find out exactly what nerve compression is, what helps, and how it can be prevented. What can help with pain, swelling and inflammation? Read more here.
Compressed nerve - symptoms
- Pain
- Tingling
- Weakness
- Other unpleasant sensations in the places to which the affected nerve leads.
The pain is sharp, burning or dull and may be accompanied by numbness in the hands or feet. Patients often describe the sensation as if their limbs are “not listening”. The discomfort may worsen with certain movements or activities, such as turning the head or stretching the back.
However, the lower limbs are not spared either, where the pain may radiate from the lower back (if it is a nerve compression in the lumbar spine or sciatic nerve compression).
Upper limb pain and numbness, on the other hand, are among the symptoms of a pinched nerve in the cervical spine. [1]

Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis. Do not use this or any other article on the internet to make a diagnosis. Do not delay seeing a doctor and address your condition early.
Description and causes of nerve compression
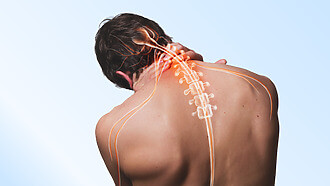
Nerve compression – what is it?
It s a condition in which a nerve is compressed or strangled by surrounding structures such as bone, muscle, tendon or swelling. This compression can lead to pain, tingling, weakness or loss of sensation in the area supplied by the nerve. Nerve compression can occur in different parts of the body and the affected area becomes a source of pain or other discomfort. [2]
Nerve compression causes
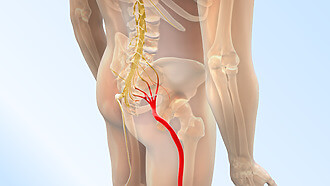
It occurs when a nerve is subjected to excessive pressure from surrounding tissues (bones, cartilage, muscles or tendons). Compression can occur in many parts of the body – the most common are pinched nerves in the lower back, pinched nerves in the hip, or general nerve root compression.
It may be related to the following situations:
- injury
- prolonged strain due to repetitive movements,
- incorrect posture while working,
- dangerous sports,
- obesity,
- certain diseases (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, inflammation).
Nerve compression also occurs when an intervertebral disc is prolapsed or when bony growths form on joints affected by arthrosis. Growths can also appear on the spine. [3],[4]
Nerve compression risk factors
Nerve pressure can affect anyone, especially in older age. However, nerve compression in the wrist area, specifically carpal tunnel syndrome, which is one of the carpal tunnel syndromes, affects women more often.
The following are also considered risk factors for nerve compression:
- diabetes,
- some monotonous jobs (for example, working on an assembly line),
- pregnancy,
- prolonged bed rest
- diseases of the thyroid gland. [5]
Diagnostics
Various procedures are used in diagnosis.
- The basis is a physical examination, which can be supplemented by blood tests.
- This is followed by imaging methods such as X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging or ultrasound.
- Electromyography (EMG) – an examination of the electrical activity of muscles and nerves – is also helpful in making a diagnosis. [6]
If the symptoms do not subside after a few days of rest and do not respond to self-medication, you should see a doctor. Warning signs include, in particular, difficulty grasping or holding objects in the hand and significant weakness of the limbs that prevents normal movement. [7]
Did you know?
- Nerve compression in the wrist (carpal tunnel syndrome) affects 6 out of 100 men and 9 out of 100 women. [8]
- Sciatica, caused by compression of the sciatic nerve, affects up to 40% of the population during their lifetime. [9]
- The likelihood of diseases increases after the age of 50. [10]
Complications when left untreated
Failure to treat it can lead to a number of complications:
- Permanent nerve damage: If a nerve is compressed for a prolonged period of time, permanent damage to the nerve fibers can occur, which can cause chronic pain, weakness, or loss of sensation.
- Muscle atrophy: If the nerve that supplies a particular muscle remains compressed, muscle weakness or loss can occur in the affected area.
- Loss of sensation: permanent loss of sensation may occur in the area supplied by the nerve.
Complications associated with movement: Untreated can affect the ability to move the affected area, which can lead to difficulty walking, grasping objects or other daily activities
Damage to the nerve
Muscle atrophy
Loss of sensitivity
Trouble with movement

We recommend not delaying treatment of nerve compression
Do not delay treatment for nerve compression and see a specialist if you have any health problems or doubts about your health. This will prevent unnecessary health complications.
Nerve compression - treatment

Rest and conservative treatment are usually sufficient for patients to fully recover within days or weeks. If the compression lasts only a short time, there are usually no long-term problems. Once the pressure on the nerve has eased, full functionality is restored. If the nerve is pinched for a longer period of time, permanent changes and chronic pain may occur. [11]
The first recommendation is usually to keep the affected area at rest. Activities or movements that caused the compression and exacerbate the discomfort should be avoided.
Further action depends on the severity and cause of the compression.
Medication
If it is necessary to take medication, it is usually:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- or corticosteroids.
These drugs relieve pain, inflammation and swelling.
Physiotherapy

Physiotherapy helps to stretch and strengthen the muscles in the affected area. This helps to relieve pressure on the nerve in question. The physiotherapist will also recommend suitable exercises for the home environment.
Braces and collars temporarily immobilise the problem area and facilitate its recovery. [12]
Massages relieve pain caused by pinched nerves and relax tight muscles. A gentle massage can have a better effect than an intense deep massage. [13]
If conservative treatment does not bring results and the problems are of a long-term nature, surgery may be the solution. Surgery is used, for example, in severe cases of intervertebral disc prolapse or carpal tunnel syndrome. [14]

Beware
Nerve compression treatment can only be determined by your doctor after considering your overall health. Therefore, do not use this article as a guide to treatment, which can only be determined by a doctor.
Prevention
The risk of diseases can be minimized by various measures.
- A pinched nerve between the ribs can be the result of improper posture. Upright posture should be thought of both standing and sitting.
- A pinched nerve in the back may be related to weakened back muscles. Regular exercise to strengthen the muscles has a very good effect in the long run.
- In activities that involve repetitive movements with unilateral loading, it is advisable to take regular breaks. [15]
- Adhering to ergonomic principles protects the back, limbs and other parts of the body. Examples are an ergonomic keyboard and mouse or a correctly positioned computer monitor. A height-adjustable chair or desk offers many relief positions. [16]
Treatment at home and self-treatment
At home it is possible not only to take preventive measures, but also to try supportive “self-treatment” in case of difficulties.
- The combination of cold and warm compresses promotes blood circulation in the affected area and can relieve pain.
- Raising the legs at the knees relieves pressure on the spine, which helps with nerve compression in the back.
- Stretching exercises and yoga relieve muscle tension and pain
- Good quality sleep contributes to the body’s recovery and can speed up the resolution of symptoms. [17]

Important information when dealing with nerve compression
It can occur in various parts of the body when a nerve is subjected to excessive pressure from surrounding tissues.
It is accompanied by pain, tingling, or decreased sensitivity at the sites to which the affected nerve leads.
The treatment mainly uses conservative methods – physiotherapy, pain and inflammation medications, orthosis or massage.
For long-term problems of a severe nature, surgical intervention may bring relief.
Summary and recommendations for nerve compression
See your physician
Nerve compression treatment is always determined by your doctor based on a general examination, an assessment of your condition and an accurate diagnosis.
Causal treatment of pain
After a general examination, your doctor will recommend treatment for the cause of nerve compression. In connection with this, they will also recommend possible lifestyle modification and further courses of action.
Relieving pain, swelling and inflammation
Symptomatic treatment focuses on the manifestations or symptoms of the disease. Such treatment can significantly improve your quality of life and support comprehensive treatment as the disease progresses.
Sources, references and literature
[1] Stuart A. Pinched (Compressed) Nerve. WebMD, 13. October 2021. Available at: https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/compressed-nerves
[2] Pinched nerve. Mayo Clinic, 22. January 2022. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pinched-nerve/symptoms-causes/syc-20354746
[3] Pinched nerve. Mayo Clinic, 22. January 2022. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pinched-nerve/symptoms-causes/syc-20354746
[4] Stuart A. Pinched (Compressed) Nerve. WebMD, 13. October 2021. Available at: https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/compressed-nerves
[5]Pinched nerve. Mayo Clinic, 22. January 2022. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pinched-nerve/symptoms-causes/syc-20354746
[6] Pinched nerve. Mayo Clinic, 22. January 2022. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pinched-nerve/symptoms-causes/syc-20354746
[7] Johnson J. How to treat a pinched nerve. Medical News Today, 11. April 2023. Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320045
[8] Petrie T. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Facts and Statistics: What You Need to Know. Verywell Health, 22. December 2022. Available at: verywellhealth.com/facts-about-carpal-tunnel-syndrome-5524726
[9] Sciatica: Of all the nerves. Harvard Health Publishing, 19. February 2016. Available at: http://www.health.harvard.edu/pain/sciatica-of-all-the-nerve
[10] Pinched Nerves. Cleveland Clinic, 7. April 2020. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/6481-pinched-nerves
[11] Pinched nerve. Mayo Clinic, 22. January 2022. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pinched-nerve/symptoms-causes/syc-20354746
[12] Pinched nerve. Mayo Clinic, 22. January 2022. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pinched-nerve/symptoms-causes/syc-20354746
[13] Johnson J. How to treat a pinched nerve. Medical News Today, 11. April 2023. Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320045
[14] Pinched nerve. Mayo Clinic, 22. January 2022. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pinched-nerve/symptoms-causes/syc-20354746
[15] Pinched nerve. Mayo Clinic, 22. January 2022. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pinched-nerve/symptoms-causes/syc-20354746
[16] Johnson J. How to treat a pinched nerve. Medical News Today, 11. April 2023. Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320045
[17] Johnson J. How to treat a pinched nerve. Medical News Today, 11. April 2023. Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320045
| Rate this article |
|
|
5/51 Reviewed by
|
How to control pain, swelling and address inflammation?
The solution may be symptomatic treatment using pulsed magnetic therapy, which targets symptoms and signs such as pain, swelling and inflammation. In addition, such treatment can support comprehensive treatment and significantly improve quality of life.
Explaining the Effects
The basic principle of Biomag 3D pulsed magnetic therapy (PEMF therapy) is the generation of electromagnetic pulses. These pulses penetrate through clothing and through the entire depth of the tissue to the point of targeted application. The pulses have specially developed biotropic parameters (e.g. frequency, shape, intensity) to best affect various health problems.
What are the effects of 3D magnetic therapy (PEMF therapy)?
- Helps relieve pain.
- Mitigates inflammation.
- Suppresses swelling.
How is the treatment applied?
The application is very simple. You select the desired therapeutic effect on the device and attach the supplied applicator to the desired application site. Magnetic therapy is usually applied 2 times a day for 20 minutes.
We will be happy to help you try this method and advise you on which device to purchase.




