Pain-relieving effect
Pulsed magnetic therapy (PEMF therapy), thanks to electromagnetic induction, conditions the formation of current in nerve fibres. This induced current causes blockage of the passage of pain perception from the site of pain through the spinal cord to the brain centres. As a result of this and some other mechanisms, pain suppression occurs. These additional mechanisms include increased endorphin production, suppression of inflammation and swelling. In addition, the myorelaxation mechanism, or the release of muscle tone (tension), is also applied.
Increased endorphin release and regulation of calcium ion transport across the cell membrane also contribute to vasodilation, analgesic effect and relaxation.
Increased lactate dehydrogenase activity in the exposed muscle was demonstrated after pulsed magnetic therapy applications. Lactate dehydrogenase conditions the breakdown of lactic acid, which provokes nerve receptors and causes pain.
Healing effect
The healing and regenerative effect of pulsed magnetic therapy (PEMF therapy) on bone and soft tissue is explained by non-specific irritation of the cytoplasmic (cell) membrane. On this membrane, a metabolic chain is activated, the key point of which is a change in the ratio of cAMP and cGMP, i.e. a change in the ratio between cyclic adenosine monophosphate and cyclic guanosine monophosphate.
In the case of the regenerative effect in bone, the applications lead to an increase in osteoclasts and a subsequent start of the bone tissue regeneration process. Pulsed magnet therapy significantly accelerates healing, activates the formation of new tissue, calcification and leads to an increase in sensitivity to parathyroid hormone, which, among other things, helps to control the level of calcium in the body.
Better blood supply to the tissue and greater oxygen saturation helps to reduce inflammation in all tissues more quickly and potentiates the effect of any antibiotic treatment.
The healing of damaged peripheral nerves is also significantly accelerated and the regeneration of neurofibrils (fibres in neurons) and the growth of central axons (fibres coming out of cells) is accelerated.
Anti-swelling effect
Edema (swelling) is caused by a disturbance of blood circulation at the level of blood capillaries with subsequent accumulation of fluid between cells.
The application of pulsed magnetic therapy (PEMF therapy) aims to counteract the main causes of swelling, i.e. increased blood pressure in the fibrous tissue (the smallest blood vessels in the body), disorders of fluid outflow from the tissue and also a possible increase in the permeability of the fibrous tissue walls.
An important role in the anti-swelling effect of PEMF therapy is played by improved perfusion, i.e. better flow through the tissues.
Acceleration of metabolism after the application of pulsed magnetic therapy allows faster absorption of swelling and at the same time there is a significant anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving effect in the area.
Myorelaxation effect
Pulsed magnetic therapy (PEMF therapy) accelerates the flushing of acid metabolites that cause painful irritation in muscles and chronic inflammation.
The washout of these metabolites is due to improved perfusion (flow through the tissues) and increased lactate dehydrogenase activity, which conditions the breakdown of lactic acid.
The application of pulsed magnetic therapy significantly reduces muscle spasm (cramps). Furthermore, the therapy reduces radicular (root) irritation, which often causes tingling and throbbing or burning pain.
By suppressing pain, PEMF therapy modifies the reflex changes of the body. By adjusting these reflexes, the body relaxes muscle spasms or contractures and spasms. This relaxation results in further pain relief.
The application of pulsed magnetic therapy therefore leads to relaxation of the skeletal muscles and improved mobility. This improvement in motion will allow further extension of the therapy, for example by making rehabilitation exercises easier.
Vasodilator effect
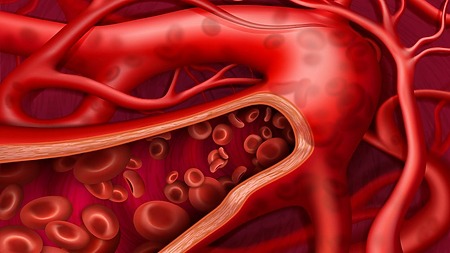
Pulsed magnetic therapy (PEMF therapy) with appropriately set parameters counteracts foaming or clumping of erythrocytes (red blood cells) that carry oxygen in the blood. The resultant effect is a re-dispersion of individual erythrocytes, thereby increasing the area capable of binding oxygen. Blood that has undergone a suitable pulsed magnetic field is thus able to oxygenate and carry oxygen to the tissues.
During PEMF therapy , parasympathetic activation and reflux of Ca2+ ions occur, which leads to relaxation of the musculature of blood vessels (especially the pre-capillary sphincters) and subsequent vasodilation.
The application of a low-frequency pulsed magnetic field affects the polarization of red blood cells with a positive charge. The polarization of blood cells affects the muscle tone of fine blood vessels, arteries and capillaries. This leads to the widening of this bloodstream (vasodilation and improved microcirculation) and thus to a better supply of oxygenated blood and nutrients to the tissues. Improved microcirculation also contributes to faster removal of toxic substances and metabolites from the tissues.
Pulsed magnetic therapy also significantly increases the partial pressure of oxygen and affects the plasticity or elasticity of blood cells. The more flexible blood cells can then pass more easily through the bloodstream. In addition, with long-term application of this method, neovascularisation, i.e. faster formation of new blood vessels, also occurs.
The application of pulsed magnetic fields also reduces the risk of blood clots (thrombi).
Metabolic - detoxifying effect

Pulsed magnetic therapy (PEMF therapy) penetrates the human tissue evenly and so thus act, as one of the few methods, also at the site of internal inflammation.
Where pulsed magnetic (PEMF) therapy is applied, it acts on each cell and induces weak electric currents in it. Due to this induction of electric currents, changes in cell surface potentials occur. The basis of any detoxification process is a better supply of nutrients and better removal of metabolic waste from the tissues.
The main detoxifying organ in the body is the liver, and therefore it is recommended to focus on it during pulsed magnetic therapy applications. Adequate hydration also supports liver function, and fluids that have undergone magnetisation can be used for this purpose. It is a process whereby the pulsed magnetic (PEMF) therapy applied to water changes the structure of the water. This water has, among other things, a better ability to bind oxygen molecules and is softer, thus better dissolving and removing waste substances and other metabolites.
