Biomag - Encyclopedia - Cervical spine pain
Cervical spine pain - symptoms, description and treatment

Author MUDr. Peter Bednarčík CSc.
Revision

Can’t turn your head in the morning? A sharp pain behind your neck prevents you from doing so? You may have a cervical spine block. A stiff neck, difficulty turning your head or even upper limb pain adversely affects work performance, limits leisure activities and brings psychological discomfort.
Find out what the causes of these problems are and what treatment options are available. How to suppress unpleasant pain in the cervical spine? Read more here.
Cervical spine pain - symptoms
- The pain may be burning or, on the contrary, resemble pressure in the affected area.
- The feeling of stiffness may spread to the shoulders and upper limbs.
- Sometimes headaches from the cervical spine are added.
- Limited mobility when turning or bending the head is also common.[1]
If cervical spine pain is caused by rapid forward movement of the head followed by rapid backward movement (typical in car accidents even at low speeds), it can add to the symptoms:
- nausea and vertigo,
- problems concentrating,
- swelling and tenderness in the cervical spine.
This type of injury is referred to as whiplash. Whiplash syndrome is an injury to the cervical spine often caused by an impact from behind. It is common for pain in the cervical spine to occur up to 6-12 hours after the accident.[2]

Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis. Do not use this or any other article on the internet to make a diagnosis. Do not delay seeing a doctor and address your condition early.
Cervical spine pain - Description and causes
What is cervical spine pain?
Cervical spine pain, technically called cervicalgia, affects the back of the neck at the site of the cervical vertebrae. However, it can also spread to the shoulders, upper back or upper limbs.
The intensity and duration of the pain depends on the cause of the problem and can last for days, months or years. Cervical spine pain affects adults of all ages and is more common in women. [3]
Cervical spine pain and headaches can occur together. Hand pain from the cervical spine is common and limits many daily activities.
Causes of cervical spine pain
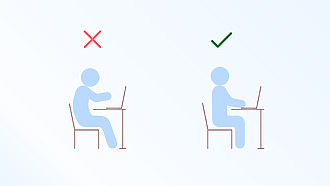
The most common causes include:
- intervertebral disc disease,
- muscle tension and cramps,
- accidents or sports injuries,
- nerve compression,
- improper posture
- inflammatory and cancerous diseases,
- other diseases (e.g. arthrosis, rheumatoid arthritis).
In many cases, excessive stress, characterised by a combination of stiff posture and muscle tension, also contributes to cervical spine pain. [4 ]Although cervical spine pain may be related to some of the above diagnoses, the causes of pain are usually not severe and can be addressed with conservative treatment. [5]
When to see a doctor
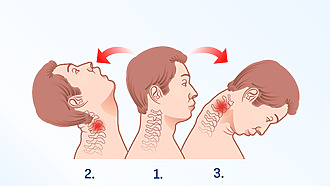
Cervical spine pain can in many cases be managed without medical attention with over-the-counter pain killers and regimens. However, if the problems last for more than a week and the pain is incompatible with normal daily activities, it is advisable to seek medical help as soon as possible.
A reason to see a doctor is also:
- pain in the cervical spine after an accident,
- weakness and numbness of the limbs,
- pain in the cervical spine and vertigo,
- impaired coordination of movement.[6],[7]
Diagnostics
Diagnosis begins with an interview with a doctor. The necessary information includes the location and type of pain, its intensity and a precise description of the associated problems. The doctor needs to know how long the pain lasts, in what situations it worsens and what brings relief. Information about any chronic diseases is also important.
Then comes the physical examination.
- The doctor palpates the painful areas and assesses their sensitivity or muscle tension.
- The examination also checks the range of motion of the neck, back and upper limbs.
Imaging methods are usually not needed. They are used if the pain persists for a long time, does not respond to conservative treatment, or if a serious disease is suspected.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) shows the spine, nerves and soft tissues. It can reveal a herniated intervertebral disc, signs of infection and tumours.
- A computed tomography (CT) scan reveals degenerative changes in the spine and shows, for example, bony prominences. It is used especially when MRI is not available. [8],[9]
- An X-ray may show some changes in the cervical spine, but is not always helpful in diagnosis. In patients with whiplash syndrome, which occurs in car crashes, X-rays show no findings because the injury is to the soft tissues and not the vertebrae.[10]
Did you know?
- Two-thirds of adults experience cervical spine pain at least once in their lifetime. [11]
- Statistics show that they occur most often in Scandinavian countries, while the fewest cases occur in some African countries.
- Cervical spine pain is more common in women than in men. The most at-risk group are those women who report poor sleep quality.[12]
Complications when left untreated
If cervical spine pain is not treated early and correctly, various complications can develop.
- The pain can persist and become chronic.
- Experts report that more than 60% of people with chronic cervical spine pain suffer from anxiety and 55% from depression.[13]
- It can impair sleep quality. [14]
- Pain and stiffness can limit movement in the neck area, which can affect the ability to turn the head or bend over
Chronic pain
Depression
Impaired sleep
Limited mobility

We recommend not delaying treatment for cervical spine pain
Do not delay treatment for cervical spine pain and see a specialist if you have any health problems or doubts about your health. This will prevent unnecessary health complications.
Treatment of cervical spine pain
Cervical spine pain is not usually a serious condition. The problem can be alleviated and resolved by conservative methods such as painkillers and various regimens[15].
Surgical treatment is warranted only in more serious cases, such as intervertebral disc prolapse or nerve oppression caused by spinal disease. [16]
Alternative treatment options include massage, acupuncture or various chiropractic procedures. [17]
Medication and exercises for cervical spine pain
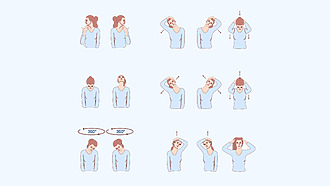
The doctor will advise you on how to relieve your cervical spine pain during your first visit to the surgery.
Pharmacotherapy includes drugs for pain, inflammation and increased muscle tension. Thanks to them, the pain subsides and the muscles can regenerate better.
The doctor or physiotherapist will recommend suitable exercises for cervical spine pain. Properly chosen exercises, accompanied by stretching, will relieve tension and help strengthen the muscles in the neck and upper back.

Beware
Treatment for cervical spine pain can only be determined by your physician after considering your overall health. Therefore, do not use this article as a guide to treatment, which can only be determined by a physician.
Lifestyle measures - treating cervical spine pain yourself

A soft foam neck brace can relieve pain at the beginning of the problem. However, it should not be used for more than three hours at a time and for more than 1-2 weeks. Too long use can lead to muscle wasting. [19]
One of the basic steps to relieve cervical spine pain is the use of hot and cold compresses.
- Place a heated towel or gel pad over the painful area for 15 minutes. The heat will relieve tension and promote circulation. The procedure can be repeated several times a day.
- A cold compress is beneficial in the case of swelling or immediately after a strain in the cervical spine that does not require medical attention.
Stress-relieving techniques in the form of breathing exercises, meditation or elements of yoga release tension, which is a common cause of pain in the cervical spine. [18]
A soft foam neck brace can relieve pain at the beginning of the problem. However, it should not be used for more than three hours at a time and for more than 1-2 weeks. Too long use can lead to muscle weakness.[19]
How to sleep with cervical spine pain
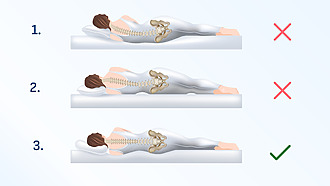
An important precaution is the correct sleeping position. A properly chosen pillow for cervical spine pain will reduce the tension on the cervical spine and relieve shoulder pain from the cervical spine.
- If you sleep on your back or side, use a pillow that supports your head so that your head and neck are at the same level as the rest of your body.
- The prone position is not suitable because of the rotation of the head to one side.[20]
Prevention
Cervical spine pain can be prevented by following various preventive measures in the field of healthy lifestyle and ergonomics.
The correct position of the head in the extension of the spine is essential – the head should not be in an unnatural forward or sideways position. The shoulders should not bend forward. When using a mobile phone or tablet, it is advisable to have the device in such a position that the head is not bent forward and the gaze is not directed downwards at the screen.
- Relief from cervical spine strain is also possible when working on a computer. Make sure that the screen is correctly positioned and at the right height. Adjust your chair, armrests and lower leg support correctly.
- When working, not just on the computer, don’t forget to take regular breaks and stretch your neck and shoulders.
Exercises for cervical spine pain, which will be shown by a physiotherapist, can be performed in home conditions and at work. The basic exercises are not complicated and their benefits are long-lasting.
More tips for preventing cervical spine pain:
- Do not carry heavy luggage over your shoulder. [21]
- Quit smoking as it slows healing and contributes to musculoskeletal damage.
- Be active and keep yourself in good physical condition. [22]

Important warnings when dealing with cervical spine pain
- Cervical spine pain is often related to poor posture, muscle tension and excessive stress.
- Pain relief comes from a combination of painkillers, appropriate exercises and warm compresses. In the long term, prevention – correct posture, an active lifestyle and adherence to ergonomics – is particularly helpful.
- Treatment can be managed on an individual basis, but if the cervical spine pain is accompanied by weakness and numbness in the limbs or dizziness, you should see a doctor as soon as possible.
Summary and recommendations for managing cervical spine pain
See your physician
Treatment for cervical spine pain is always determined by your physician based on a general examination, an assessment of your condition and an accurate diagnosis.
Causal treatment of cervical spine pain
After a general examination, your physician will recommend treatment for the cause of your arthritic joints. In connection with this, he will also recommend possible lifestyle modification and further course of action.
Relieve pain, swelling and inflammation
Symptomatic treatment focuses on the manifestations or signs (symptoms) of the disease. Such treatment can significantly improve your quality of life and support comprehensive treatment as the disease progresses.
Sources, references and literature
[1] Neck Pain. Cleveland Clinic, 9. December 2022. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/21179-neck-pain
[2] Whiplash. Healthdirect Australia, May 2022. Available at: https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/whiplash
[3] Neck Pain. Cleveland Clinic, 9. December 2022. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/21179-neck-pain
[4] Neck Pain. Cleveland Clinic, 9. December 2022. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/21179-neck-pain
[5] Neck Pain. Mayo Clinic, 25. August 2023. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/neck-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20375581
[6] Michael A. P. Neck Pain. American Association of Neurological Surgeons. Available at: https://www.aans.org/en/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Neck-Pain
[7] Neck Pain. Cleveland Clinic, 9. December 2022. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/21179-neck-pain
[8] Neck Pain. Mayo Clinic, 25. August 2023. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/neck-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20375581
[9] Neck Pain. Cleveland Clinic, 9. December 2022. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/21179-neck-pain
[10] Whiplash. Healthdirect Australia, May 2022. Available at: https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/whiplash
[11] Elbinoune I., Amine B., Shyen S. et al. Chronic neck pain and anxiety-depression: prevalence and associated risk factors. Pan Afr Med J. 2016 May 27; 24: 89, doi: 10.11604/pamj.2016.24.89.8831. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5012832/
[12] Kazeminasab S., Nejadghaderi S. A., Amiri P. et al. Neck pain: global epidemiology, trends and risk factors. BMC Musculoskeletal Disord. 2022 Jan 3;23(1):26, doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04957-4. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8725362/
[13] Elbinoune I., Amine B., Shyen S. et al. Chronic neck pain and anxiety-depression: prevalence and associated risk factors. Pan Afr Med J. 2016 May 27; 24: 89, doi: 10.11604/pamj.2016.24.89.8831. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5012832/
[14] Kazeminasab S., Nejadghaderi S. A., Amiri P. et al. Neck pain: global epidemiology, trends and risk factors. BMC Musculoskeletal Disord. 2022 Jan 3;23(1):26, doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04957-4. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8725362/
[15] Michael A. P. Neck Pain. American Association of Neurological Surgeons. Available at: https://www.aans.org/en/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Neck-Pain
[16] Neck Pain. Cleveland Clinic, 9. December 2022. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/21179-neck-pain
[17] Neck Pain. Mayo Clinic, 25. August 2023. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/neck-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20375581
[18] Neck Pain. Cleveland Clinic, 9. December 2022. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/21179-neck-pain
[19] Neck Pain. Mayo Clinic, 25. August 2023. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/neck-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20375581
[20] Neck Pain. Cleveland Clinic, 9. December 2022. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/21179-neck-pain
[21] Neck Pain. Mayo Clinic, 25. August 2023. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/neck-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20375581
[22] Neck Pain. Cleveland Clinic, 9. December 2022. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/21179-neck-pain
| Rate this article |
|
|
5/51 Reviewed by
|
How to control pain, swelling and address inflammation?
The solution may be symptomatic treatment using pulsed magnetic therapy (PEMF therapy), which targets symptoms and signs such as pain, swelling and inflammation. In addition, such treatment can support comprehensive treatment and significantly improve quality of life.
The principle of therapy
The basic principle of Biomag 3D pulsed magnetic therapy (PEMF therapy) is the generation of electromagnetic pulses. These pulses penetrate through clothing and through the entire depth of the tissue to the point of targeted application. The pulses have specially developed biotropic parameters (e.g. frequency, shape, intensity) to best affect various health problems.
What are the effects of 3D magnetic therapy (PEMF therapy)?
- Helps relieve pain.
- Mitigates inflammation.
- Suppresses swelling.
How is the treatment applied?
The application is very simple. You select the desired therapeutic effect on the device and attach the supplied applicator to the desired application site. Magnetic therapy (PEMF therapy) is usually applied 2 times a day for 20 minutes.
We will be happy to help you try this method and advise you on which device to purchase.




